The first signs of cervical osteochondrosis are quite difficult to notice. Often they cause so little discomfort that a person does not pay attention to them and does not rush to consult a doctor. In other cases, the symptoms are confused with simple fatigue or a mild cold:
- increasing neck pain;
- feeling of heaviness in the back of the head;
- slight tingling of the hands.
These signs appear in thousands of people every day, but few can recognize them as developing cervical osteochondrosis.
important! Remember that the disease develops slowly and in the first stages it is much easier to limit the progression of destructive processes than to treat an advanced stage!
Who is at risk?
Osteochondrosis develops not only in those who lead a sedentary life. Athletes from fields such as classical wrestling, judo, freestyle wrestling and sambo also suffer from this disease. The disease develops due to critical loads on the spine in the cervical region (constant falls and blows, high mobility of the neck). It is important to keep in mind that osteochondrosis is often diagnosed before the age of 35 - over 86% of cases.
How the disease develops
Currently, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is much more common than other pathologies of the spine. This is due to the greater mobility of the neck. As the disease progresses, severe pain appears, which worsens a person's life. Osteochondrosis progresses slowly, but surely leads to degenerative changes in the bone tissues of the spine. There are four stages of development of the disease:
- The first stage is characterized by an almost complete absence of symptoms. The disease can only be diagnosed during a routine examination. Sometimes a slight pain may occur, which many interpret as signs of stress or fatigue. At the first stage, the destruction of the nucleus pulposus occurs, due to which the vertebrae begin to bear the load worse. As a result, degenerative-dystrophic processes develop. Among the first symptoms are: a mild headache that quickly disappears, spasm syndrome "inside the neck", significant muscle tension in the upper back.
- In the second stage of the disease, cracks appear on the sides of the discs due to stress. They are still not very deep, but already contribute to squeezing the core. During diagnosis, a protrusion is often found and the height of the disc decreases. This stage is characterized by frequent and prolonged pain. A person loses strength, some areas of his face begin to go numb, and stiffness of movements develops due to fear of new painful sensations.
- The third stage is characterized by the formation of a hernia in the cervical region between the vertebrae. All the tissues and vessels located in this area are also affected - veins, muscles, nerves, arteries. The pain smoothly flows and spreads from the neck to the occipital region. Particular sensitivity occurs when moving the head. Patients also begin to complain of dizziness due to insufficient blood flow in the vertebral artery.
- In the fourth stage, osteophytes are formed - bone tissue increases in width, because the body and brain literally send signals requiring an increase in area to distribute the load. As a result, the nerves of the vertebrae are compressed, the cavities between the vertebrae are reduced, severe stiffness occurs, and sometimes the inability to move. All adjacent joints are damaged. In order to eliminate the causes and "hold" cervical osteochondrosis at this stage, it will be necessary to carry out long-term and difficult treatment, including surgical intervention.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis is an important process that will help limit the degradation of the cervical vertebrae, alleviate complications and preserve the quality of life. But in order to identify the pathology, you need not only to observe the symptoms, but at least once a year to carry out diagnostics and take the necessary tests.
Features of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Even minor changes in the vertebrae, ligaments and intervertebral discs lead to disruption of the functioning of the nerve endings. Blood vessels are also affected. All of them connect directly to the brain and other organs, from where the unpleasant symptoms arise.
important! It is the compression of blood vessels and nerves that leads to discomfort and severe pain.
Clinical symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are divided into three groups:
- the first group is characterized by neurological manifestations of pathology that arise due to the impact of inflammatory processes and changes occurring in the tissues of the peripheral part of the nervous system;
- the second group is related to the impact of the processes on the spinal cord;
- The third group includes signs that depend on disruption of the processes in the nerve endings that lead to the brain.
As soon as disturbances occur in the peripheral nervous system, a person begins to experience pain. They don't always start suddenly and last a long time, but they all start from the same place - inside the neck. The pain is not similar to muscle pain, there is no relaxation when kneading.
In most cases, with damage to the peripheral system, a feeling of shortness of breath appears. Patients feel as if they have a "lump" in their throat and it becomes difficult for them to breathe. The pain is characterized as unexpressed, dull, constant tension in the muscles is felt. Sometimes after a night's sleep, the pain intensifies.
The progression of the disease leads to the spread of symptoms. After the head and neck, the hands begin to suffer:
- feeling weak;
- numbness appears in one or more fingers;
- then large parts of the hands go numb.
If you feel pain and pressure in the area of the heart, you can talk about the development of cervico-thoracic osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis is often misidentified as angina or neuralgia. It is mainly characterized by symptoms such as:
- cough;
- stomach pains;
- discomfort in the liver;
- pain in the lungs.
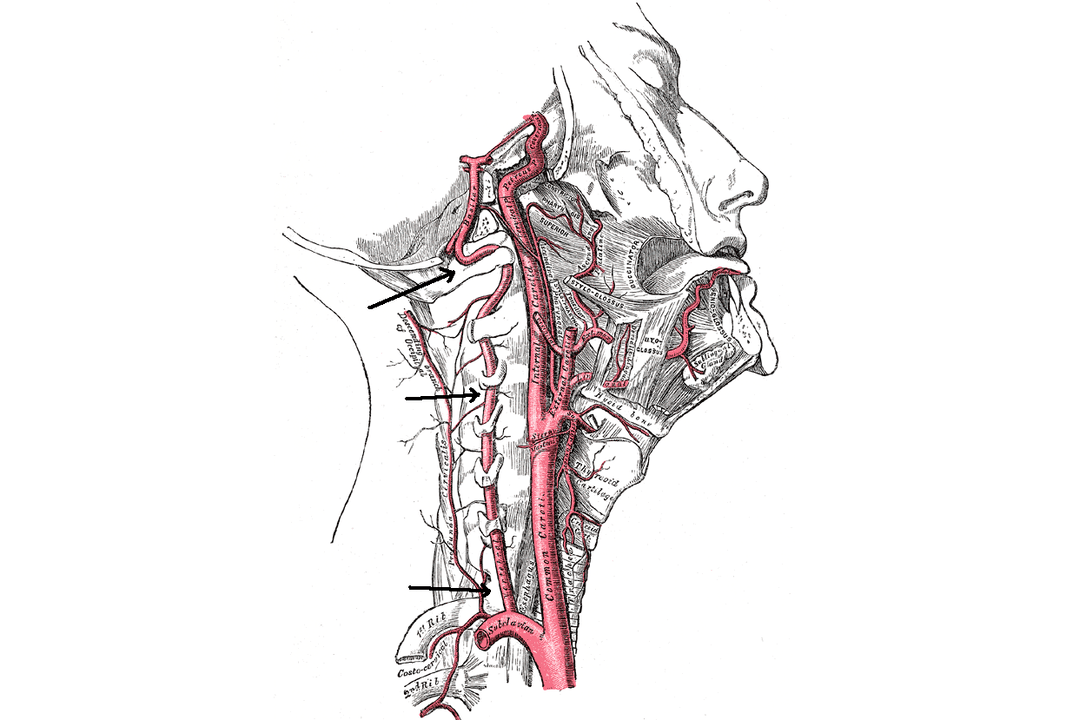
As soon as the vertebral artery connects to the destructive process (supplying the brain with oxygen), symptoms from the brain begin to appear. As the disease progresses, it becomes pinched and cannot function normally. Thus, vertigo develops, vision deteriorates, tinnitus appears.
The use of conventional painkillers rarely helps with headaches with cervical osteochondrosis.
Physical activity and frequent nervous tension can provoke an exacerbation of the pathology. Symptoms of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis:
- increasing irritation;
- sensitive and interrupted sleep;
- rapid fatigue.
If a person is diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia, then the symptoms intensify: neuroses develop, blood pressure jumps. The diagnosis can also indicate the development of cervical osteochondrosis, so it is necessary to pass all the tests, undergo an MRI and take other pictures of the cervical spine.
It is almost impossible to independently diagnose cervical osteochondrosis based on symptoms. Given that the first stage occurs practically without visible signs, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations. At the first signs of the disease, you should start treatment, following the doctor's recommendations. Even if the disease has not yet "played out" and does not cause tangible problems.
Syndromes
For an accurate diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, a correct justification of the symptoms is necessary. Based on tests, imaging and examination, the doctor must accurately determine the causes of the symptoms. All of them are associated with certain syndromes.
Humeroscapular periarthritis
The syndrome is characterized by severe pain and muscle contracture in the area of one of the shoulder joints. In left-handed people, the left shoulder joint is usually affected, and in right-handed people, the right. Features of the pain syndrome:
- permanent;
- pains;
- pains.
In most cases, the pain worsens at night. If you move your arm to the side or put it behind your back, the pain will also increase. Sometimes the pain is felt in the whole arm, in the occipital and scapular region.
During the examination, the doctor often notices tension in the joint area, and during palpation, the patient feels severe pain in the muscles. In some cases, the doctor notices seals and small nodules during palpation, there is slight swelling of the affected shoulder.
Radicular syndromes
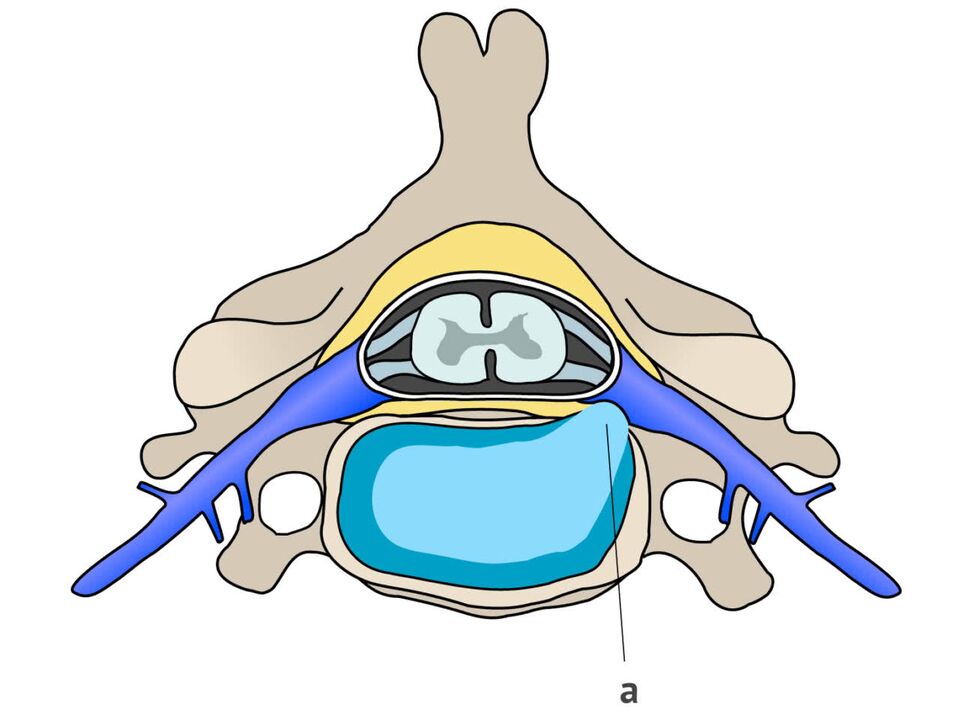
The syndrome can develop with spinal root damage. It usually appears a few years after the onset of osteochondrosis. In the vertebrae and discs, irreversible destruction occurs: the cavity consisting of nerves and vessels decreases, as the cartilage thins or an intervertebral hernia is formed. Osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome is characterized by certain symptoms:
- the pain is observed in the forearm, in the area of the scapula and moves to the front of the chest;
- it becomes difficult to move the neck, pain and stiffness are felt;
- The sensitivity of the skin of the hands worsens, it tingles and a "goosebumps" sensation appears;
- a person cannot raise his hand from the side of the affected parts.
Irritative-reflex syndrome
The syndrome is characterized by a slightly burning, sharp pain in the back of the head and neck. Appears when moving the head after a long period of immobility, for example when working on a computer. Discomfort is felt in the shoulder joints, as well as in the chest area.
Cardiac syndrome
The syndrome is often confused with angina pectoris, as the symptoms of the diseases are almost identical. This happens because the pain and contractions of the muscle tissue in the area of the heart occur due to compression of the roots in the lower parts of the cervical spine. Hence the similarity of diseases.
The syndrome is characterized by pain that comes in bouts and can last from 10-15 minutes to several hours. They significantly increase during sudden movements (turning, coughing, sneezing). Often, the cardinal syndrome is characterized by the development of tachycardia, and coronary dilators do not cope with pain relief. There are also no signs characteristic of circulatory disorders on the cardiogram.
Vertebral artery syndrome
The role of the vertebral artery is to supply the brain and spinal cord. In the syndrome, the work of the periarterial sympathetic plexus is disturbed. The syndromic picture looks like this:
- headache of varying intensity;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus (staggering, loss of balance);
- mild and severe dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pharyngolaryngeal and eye symptoms (deterioration of vision, the appearance of a veil before the eyes).
In vertebral artery syndrome, burning pain often occurs not only in the neck, but also in the back of the head. A feeling of lethargy, resentment and irritability develops. Anxiety levels rise, sleep and memory can be impaired.
Thus, in order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to determine which syndrome is the basis of cervical osteochondrosis. Based on specific symptoms, test results, photographs and palpation, an experienced doctor will be able to accurately determine the characteristics of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment.



















